Configure git repositories
Introduction
Build from a Git repository allows you to build Gatling simulations directly from a source repository, such as GitHub, GitLab, or BitBucket without needing to package them first. This feature is particularly useful for teams that prefer to manage their Gatling projects in a source control system and want to streamline the process of running tests.
Simulations are built and stored in your private network, using the Private Locations and Private Packages features of Gatling Enterprise Edition. This approach eliminates the need for manual packaging and uploading of simulation files, enabling a more efficient workflow for performance testing.
The following sections detail how to configure the Control Plane for Build from a Git repository, including pre-requisites, git authentication, and build tool configurations. Once configured, you can create simulations in the Gatling Enterprise Edition UI.
Pre-requisites
Control Plane Docker image
Use the dedicated gatlingcorp/control-plane:latest-builder image.
latest-builder tag.CPU and memory resources
Allocate adequate CPU and memory resources according to your project’s compilation needs. 4 CPUs and 4Gb of memory should be a strict minimum.
Filesystem
Beware that compiling code and generating packages generates tons of small files that we need to delete afterward to not fill the filesystem.
Please avoid using XFS whose performance is very bad for deleting tons of small files.
Private Locations
Build from a Git repository is only compatible with Private Locations. Ensure these are configured first.
Private Packages
Build from a Git repository requires a configured private storage location to store ephemeral packages. These will be automatically deleted once they are deployed on the load generators.
Build tool
Required Gatling plugins versions
We require the following minimum versions:
| Build Tool | Gatling Plugin | Minimum Version |
|---|---|---|
| Maven | gatling-maven-plugin |
4.16.3 |
| Gradle | io.gatling.gradle |
3.13.5.4 |
| sbt | gatling-sbt |
4.13.3 |
| npm | @gatling.io/cli |
3.13.501 |
Configuration
If your infrastructure blocks access to online dependency repositories such as Maven Central, Gradle Portal or NPM Registry and instead requires dependencies to be downloaded from a corporate repository, please make sure to configure your build tool accordingly.
In particular, for maven, you might want to mount a /app/.m2/conf/settings.xml with a mirrors configuration so Maven Central is not even tried and cause timeouts.
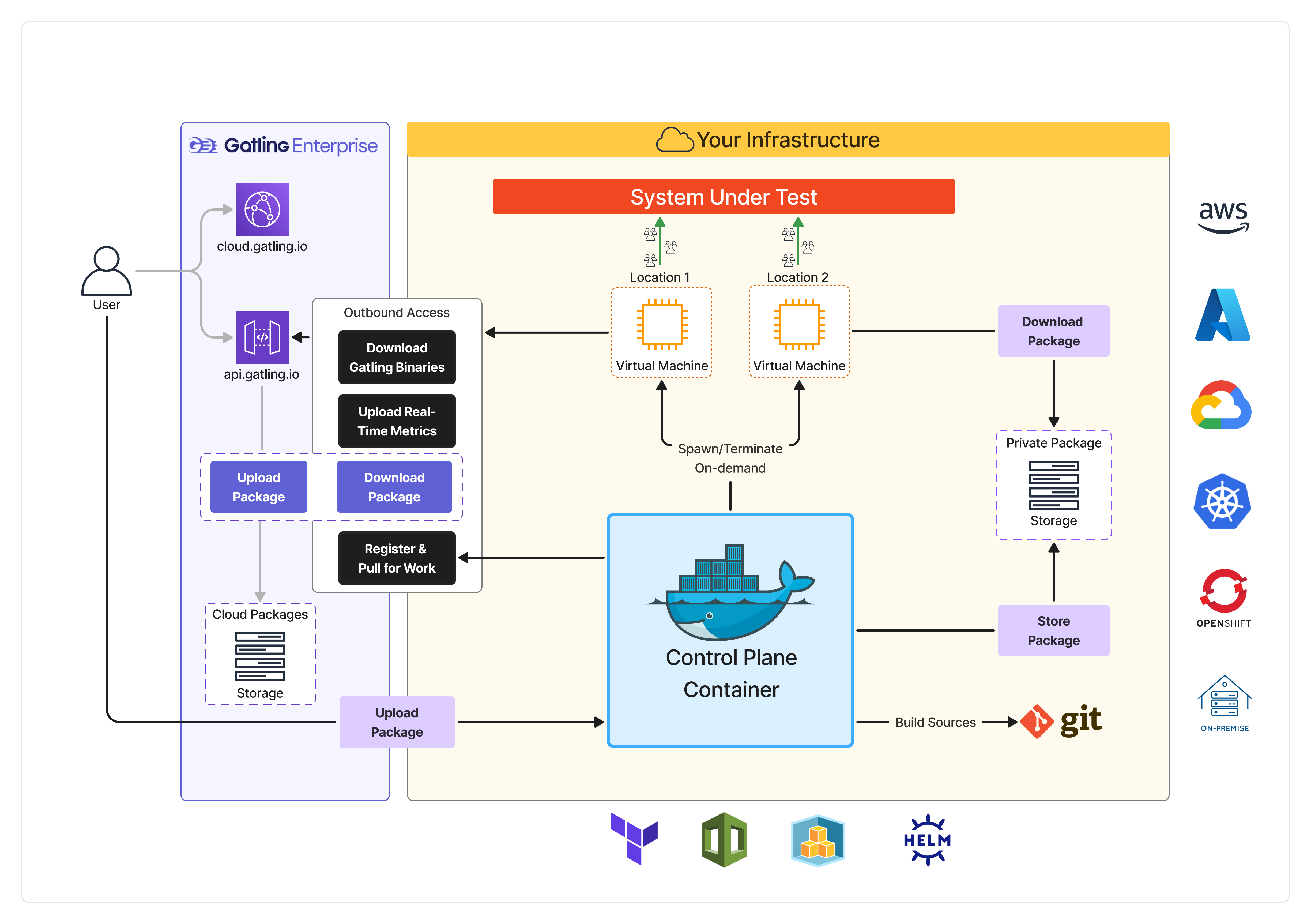
Architecture
The Build from a Git repository feature operates within the Gatling Enterprise Edition architecture, leveraging the Control Plane to manage builds and simulations.
The Control Plane interacts with your source repository to fetch simulation code, compiles it using the specified build tool, and stores the resulting artifacts in your private storage location.
This process is triggered when you start a simulation in the Gatling Enterprise Edition UI, allowing you to run tests directly from your source code without manual packaging.
After run completion, the test package is deleted from the private storage location, thus each run requires a fresh build from the source repository.
This ensures that you always test the latest version of your simulations.
Build Concurrency
By default, the Control Plane is configured to allow only one build to be performed at a time.
This default setting means that if multiple simulations requiring a build from source are started simultaneously, subsequent builds will enter a queue and must wait for the preceding build to complete before starting.
A build timeout of 10 minutes is enforced. The build process must successfully complete within this timeframe.
You can increase the maximum number of concurrent builds by adjusting the following configuration:
control-plane {
# ...
builder {
# Define the maximum number of builds the control plane can perform concurrently.
# Increase this value to allow more builds to run in parallel.
max-concurrency = 1 # Change '1' to the desired concurrency level (e.g., 2, 4)
}
}
Make sure your Control Plane’s underlying infrastructure (CPU and memory requirements) can support simultaneous build operations,
Git authentication
The following sections detail how to configure the Control Plane for Build from a Git repository.
Cloning over SSH
When authenticating with Git over SSH, you can use an SSH key for secure access. This method provides a secure way to authenticate without exposing credentials.
SSH Configuration Mount
Set up your SSH key within the control plane configuration block:
control-plane {
# ...
builder {
git.global.credentials.ssh {
key-file = <keyFile>
user-known-hosts-file = <userKnownHostsFile> # (optional – omit this line to disable strict host checking)
}
}
}
-
Mount the SSH key file at the
git.global.credentials.ssh.key-filepath inside the container.
Ensure that/app/.ssh/id_gatlinghas permission 400:- Owner: Read
- Group: No access
- Others: No access
-
Make sure the mounted
.sshdirectory is owned by the Gatling user (UID 1001):
chown -R 1001 /app/.ssh
- If
git.global.credentials.ssh.user-known-hosts-fileis set, mount aknown_hostsfile to the specified path.
How to Add Hosts to user-known-hosts-file
Use ssh-keyscan to populate the file mounted at user-known-hosts-file:
ssh-keyscan github.com gitlab.com >> ~/.ssh/known_hosts
Cloning over HTTPS
Configuring a custom Certificate Authority
If your git repository HTTPS server uses a private key issued by an internal CA, its certificate must be trusted on the git client side.
You have to :
- expose the CA certificate to the container, typically from a mounted directory
- this certificate must be in PEM format
- on your container, set the
GIT_SSL_CAINFOenv var with the absolute path to the CA certificate from inside the container
For more information, please check the git documentation and the cURL documentation (which is what git uses underneath).
Configuring git credentials
When authenticating with Git over HTTPS (via password or token), you can specify credentials in the Control Plane configuration file (e.g., control-plane.conf):
control-plane {
# ...
builder {
git.global.credentials.https {
username = <username> # (optional)
password = <token>
}
}
}
Security Best Practices:
- Use personal access tokens instead of passwords whenever possible.
- Limit token permissions to read-only access.
- Never include credentials in repository URLs within Gatling Enterprise Edition.
Caching
Local caches
We strongly recommend that you mount all the following directories on a persisted volume so you don’t have to re-download all the dependencies on each container reboot:
/app/.m2/app/.gradle/app/.sbt/app/.cache/coursier/app/.ivy2/app/.npm
Private storage build cache
If your Gatling project takes a long time to build and doesn’t change on every run, you may want to configure caching on your private storage location. Refer to the Build Caching section for your storage provider.
Once configured, a cached build is reused when the following conditions are met:
- The Git repository URL has not changed
- The target branch HEAD commit has not changed
- The build command has not changed
- The configured time-to-live has not expired

