Kubernetes
Learn how to configure Kubernetes injectors for Gatling Enterprise.
A Kubernetes/OpenShift Pool is a reference to your Kubernetes infrastructure.
Credentials settings
Kubernetes pools configuration gains access to the cluster through the credentials settings:
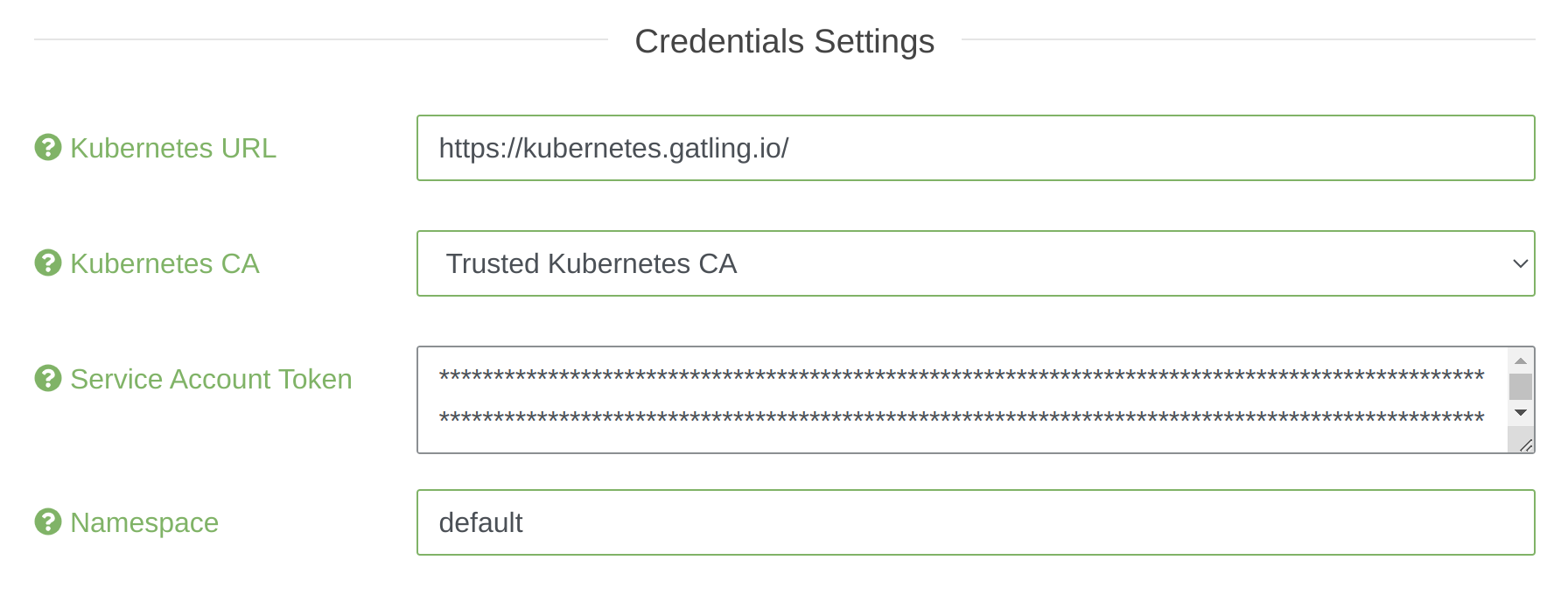
- Kubernetes URL: The url of your Kubernetes API with the protocol
- Kubernetes CA: The certificate of your Kubernetes API (optional, trusted by default)
- Service Account Token: The token of your service account which has edit permissions on the namespace below (see the minimal permissions)
- Namespace: The namespace/project name in which injectors will be spawned
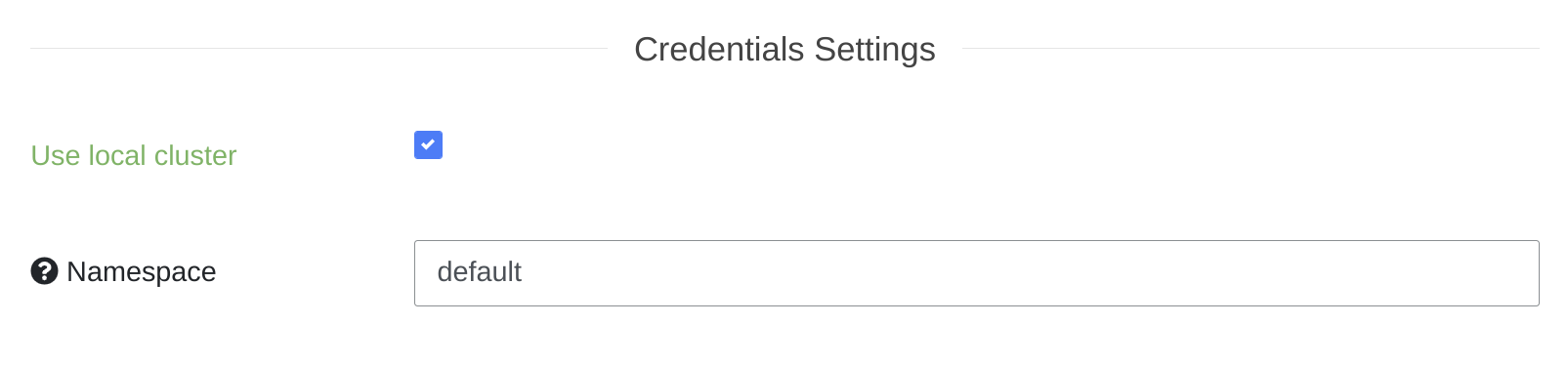
If your instance of Gatling Enterprise is deployed inside a kubernetes cluster, and you want to deploy your injectors in the same cluster,
you can enable the local cluster mode:
Instance settings
To configure the type of instances you want to spawn, you need to fill the form below:

- Connection:
- Ingress: exposes HTTP and HTTPS routes from outside the cluster to injectors within the cluster
- TLS secret name: the optional secret containing a certificate used by the ingress TLS secrets documentation
- Class name: the optional class name of the ingress, used for the ingress controller Ingress class documentation
- Route: (OpenShift extension) exposes HTTP routes (HTTPS not supported) from outside the cluster to injectors within the cluster.
- Secured: allow you to add the desired certificate on the route OpenShift secured routes documentation
- Certificate: Certificate associated with the route
- Certificate key: Certificate key associated to certificate
- CA Certificate: Certificate authority signing the certificate
- Ingress: exposes HTTP and HTTPS routes from outside the cluster to injectors within the cluster
- Docker Image: Docker image that will be used for injectors. You can use our certified Docker images if your Kubernetes cluster has access to Docker Hub, or build your own with gatling/frontline-injector-docker-image. Our certified images are available for the
linux/amd64andlinux/arm64platforms (Docker will automatically select the correct image variant). - Image pull secret: Recommended approach to run containers based on images in private registries and / or to not be limited by rate limits
- CPU request: The minimum number of cores that you need for each injector, express as cpus
- CPU limit: The limit of cores that you don’t want each injector pod to exceed, express as cpus
- Memory request: The minimum memory that you need for each injector
- Memory limit: The maximum memory that you need for each injector
- Custom labels: Optional labels to add to all injector pods, services, ingresses and routes
- Node selector: An optional nodeSelector to add to each injector pod (they will only run on nodes with matching labels)
- Environment variables: The environment variables configured for each injector
Limits and requests for memory are measured in bytes. You can express memory as a plain integer or as a fixed-point integer using one of these suffixes: E, P, T, G, M, K. You can also use the power-of-two equivalents: Ei, Pi, Ti, Gi, Mi, Ki.
Tolerations settings
To configure torelations, you may fill:
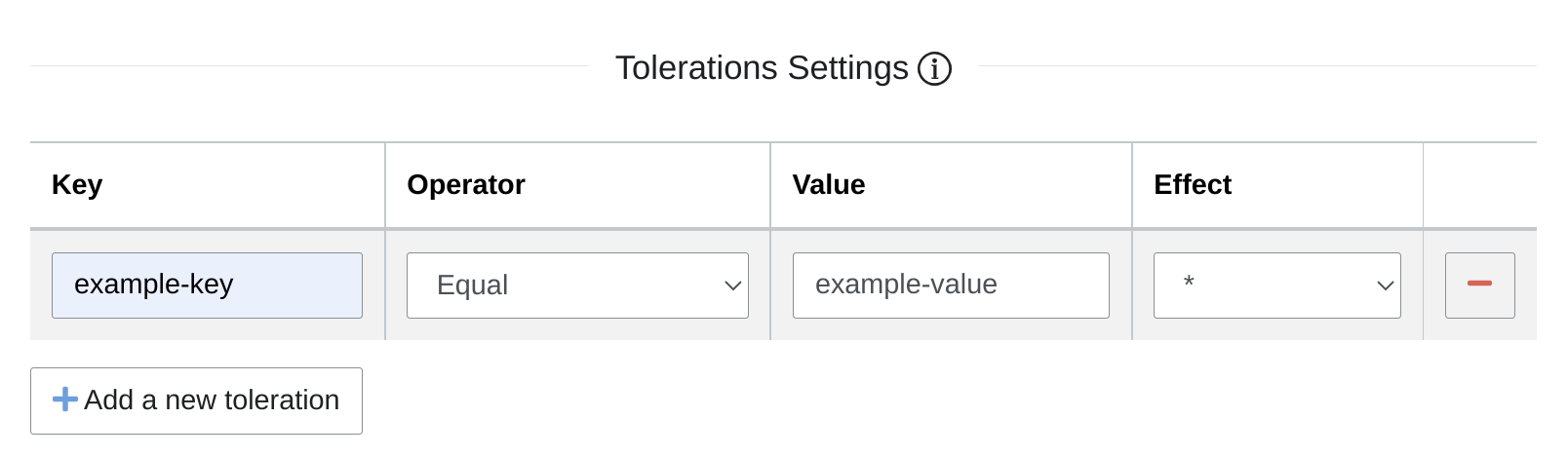
- Key: toleration key
- Operator: Either exists or equal
- Exists: Any node matching the key will have the effect applied, no need to specify the value
- Equal: Any node matching the key with the given value will have the effect applied
- Value: The value associated with the key
- Effect: Applied effect based on key/value operator
- *: Match all effects
- NoSchedule, PreferNoSchedule, NoExecute: Match node taint with those effects
Minimal permissions for Gatling Enterprise service account
Service account associated to the service-account-token must be binded with permissions to manage services, nodes, routes, ingresses and pods (depending on your needs).
To obtain the service account token, use the following kubectl command:
kubectl --namespace=frontline get secret frontline-sa-token --output jsonpath={.data.token} | base64 --decode
Below, you can find a commented configuration file containing all needed permissions.
frontline, must be updated accordingly based on the namespace you configure on your pool.# Dedicated namespace for Gatling Enterprise
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: frontline
---
# Service account named frontline-sa
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: frontline-sa
namespace: frontline
---
# Service account token
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: frontline-sa-token
namespace: frontline
annotations:
kubernetes.io/service-account.name: frontline-sa
type: kubernetes.io/service-account-token
---
# Role containing needed permissions
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: frontline-manage-injectors
namespace: frontline
rules:
# Used to check the pool configuration
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["namespaces"]
verbs: ["get"]
# Needed for management of injectors instances
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["services", "pods", "pods/exec"]
verbs: ["create","delete","get","list","patch","update","watch"]
# Only for usage of Ingresses, use "extensions" instead of "networking.k8s.io" before Kubernetes 1.22
# See https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx/user-guide/k8s-122-migration/
- apiGroups: ["networking.k8s.io"]
resources: ["ingresses"]
verbs: ["create", "delete", "get", "list", "watch"]
# Only for usage of OpenShift Routes
- apiGroups: ["route.openshift.io"]
resources: ["routes", "routes/custom-host"]
verbs: ["create", "delete", "get", "list", "watch"]
---
# Bind role to the service account
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: frontline-role-binding
namespace: frontline
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: frontline-manage-injectors
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: frontline-sa
namespace: frontline
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: frontline-sa-token
annotations:
kubernetes.io/service-account.name: frontline-sa
type: kubernetes.io/service-account-token

